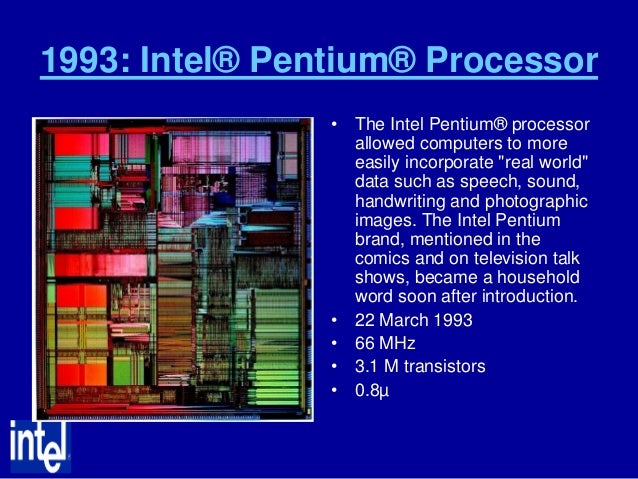
Computer Processors
Today, computers are a part of our lifestyle, but the first computer that was used was developed at the University of Pennsylvania in the year 1946! It had an ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer) processor. The reprogramming feature that is so extensively used today, was introduced by Alan Turing and John von Neumann with their teams. The von Neumann architecture is the basis of modern computers.
From the development of the first microprocessor - Intel's 4004 to the latest ones - the microprocessors have come a long way. Here, we look into the story so far.
From the development of the first microprocessor - Intel's 4004 to the latest ones - the microprocessors have come a long way. Here, we look into the story so far.
Types and Characteristics of Processors
•Two major processor manufacturers
"Intel" and "AMD"
processors is many work of our PC or LAPTOP and also performance or compatibility
with motherboards are -:
–Clock speed the processor supports
–Processor speed
–Socket and chipset the processor can use
–Processor architecture
–Multiprocessing abilities
•Dual processors
•Multi-core processing
•Multithreading
•Basic components
–Input/output (I/O) unit
•Manages data and instructions entering and leaving the processor
–Control unit
•Manages all activities inside the processor
–One or more arithmetic logic units (ALUs)
•Performs all logical comparisons, calculations
How a Processor Works
Processor Frequency
CPU clock speed, or clock rate, is measured in Hertz — generally in gigahertz, or GHz. A CPU's clock speed rate is a measure of how many clock cycles a CPU can perform per second. For example, a CPU with a clock rate of 1.8 GHz can perform 1,800,000,000 clock cycles per second.
•Multiplier
–Factor multiplied against system bus frequency
•Determines processor frequency
–System bus frequency × multiplier = processor frequency
•Processor sold today contain ALUs and registers that can process 32 bits or 64 bits
at a time.
•Three categories of processors:
–32-bit processors – known as x86 processors
•Can handle 32-bit instructions from OS
–Hybrid processors – known as x86-64 processors
•Can handle a 32-bit OS or a 64-bit OS
•AMD produced the first one (called AMD64)
–64-bit processors – known as x64 processors
•Require a 64-bit OS and can handle 32-bit applications only by
simulating 32-bit
processing.
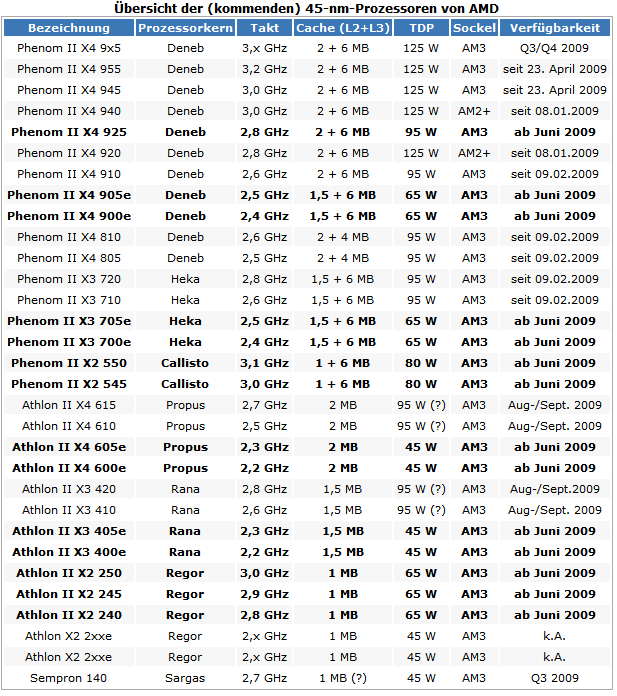
- WHAT IS "AMD {Advanced Micro Devices }"
AMD is the second-largest supplier and only significant rival to Intel in the market for x86 based microprocessors. Since acquiring ATI in 2006, AMD and its competitor Nvidia have maintained a duopoly in the discrete Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) market.
AMD Processor
Performance
If you're building a gaming PC, truthfully you should be using a discrete graphics card, or GPU (graphics processing unit), rather than relying on a CPU’s integrated graphics to run games as demanding as Middle Earth: Shadow of War.
Still, it’s possible to run less graphically intense games on an integrated GPU if your processor has one. In this area, AMD is the clear winner, thanks to the release of the Ryzen 5 2400G that packs powerful discrete Vega graphics that outperforms Intel’s onboard graphic technology by leaps and bounds.
Yet, as we mentioned before, Intel has officially started shipping its high-end H-series mobile CPU chips with AMD graphics on board. In turn, this means that hardier laptops powered by Intel can now be thinner and their accompanying silicon footprints will be over 50% smaller, according to Intel client computing group vice president Christopher Walker.
All of this is accomplished using Embedded Multi-Die Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) technology, along with a newly contrived framework that enables power sharing between Intel’s first-party processors and third-party graphics chips with dedicated graphics memory. Even so, it’s too early to tell whether this is a better solution than the purebred AMD notebooks slated for the end of this year.
Intel might be aiming to shake things up though as it has announced that it’s planning on releasing a GPU aimed at gamers by 2020. And, if we could see Intel putting some of that effort into improving integrated graphics.
Still, if all you're looking to do is play League of Legends at modest settings or relive your childhood with a hard drive full of emulators (it's okay, we won't tell), the latest Intel Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake or AMD A-Series APU processors for desktops will likely fare just as well as any forthcoming portable graphics solution.
On the high-end, especially in cases where you don’t need to worry about on-board graphics, Intel’s processors are typically on top – its Core i9-9900K handily beats out the workstation-class Ryzen Threadripper 2970WX for less than half the price.
AMD typically provides better multi-threading performance, as a result of higher core and thread counts. Ryzen CPUs also offer more PCIe lanes, which come in handy if you want multiple NVMe SSDs alongside SLI and CrossFire multi-GPU performance.
While there is no clear winner in the graphics department, survey says AMD is the better option for integrated graphics, while hardcore gamers who don’t mind shelling out the extra cash for a GPU will find that Intel is better for gaming alone – although with Ryzen 2nd Generation AMD is closing that gap. Meanwhile, AMD is superior for carrying out numerous tasks at once.
Graphics
If you're building a gaming PC, truthfully you should be using a discrete graphics card, or GPU (graphics processing unit), rather than relying on a CPU’s integrated graphics to run games as demanding as Middle Earth: Shadow of War.
Still, it’s possible to run less graphically intense games on an integrated GPU if your processor has one. In this area, AMD is the clear winner, thanks to the release of the Ryzen 5 2400G that packs powerful discrete Vega graphics that outperforms Intel’s onboard graphic technology by leaps and bounds.
Yet, as we mentioned before, Intel has officially started shipping its high-end H-series mobile CPU chips with AMD graphics on board. In turn, this means that hardier laptops powered by Intel can now be thinner and their accompanying silicon footprints will be over 50% smaller, according to Intel client computing group vice president Christopher Walker.
All of this is accomplished using Embedded Multi-Die Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) technology, along with a newly contrived framework that enables power sharing between Intel’s first-party processors and third-party graphics chips with dedicated graphics memory. Even so, it’s too early to tell whether this is a better solution than the purebred AMD notebooks slated for the end of this year.
Still, if all you're looking to do is play League of Legends at modest settings or relive your childhood with a hard drive full of emulators (it's okay, we won't tell), the latest Intel Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake or AMD A-Series APU processors for desktops will likely fare just as well as any forthcoming portable graphics solution.
On the high end, such as in cases where you'll be pairing your CPU with a powerful AMD or Nvidia GPU, Intel’s processors are typically better for gaming due to their higher base and boost clock speeds. At the same time, though, AMD provides better CPUs for multi-tasking as a result of their higher core and thread counts.
While there is no clear winner in the graphics department, survey says AMD is the better option for integrated graphics, while hardcore gamers who don’t mind shelling out the extra cash for a GPU will find that Intel is better for gaming alone. Meanwhile, AMD is superior for carrying out numerous tasks at once.
INTEL Processor
Performance
When looking at a new processor for your PC, you will likely compare processors from Intel and AMD. Intel's most popular processors in the desktop world are theCore i3, i5, and i7 product lines. The Core i3 is entry level, and Core i7 processors are the more powerful hyper-threaded quad-core options.
Intel Core i3 desktop processors have four cores. Core i7 processors have both Turbo Boost and Hyper-Threading. They may have six cores like anIntel Core i5, but can operate as if they have 12 cores. Intel Core i9 CPUs, meanwhile, offer eight cores.
World's fastest processor is an overclocked beast [video] AMD announced that their new 8-core Bulldozer FX processor clocked a record speed of 8.429GHz with the help of liquid nitrogen and helium.
World's fastest processor is an overclocked beast [video] AMD announced that their new 8-core Bulldozer FX processor clocked a record speed of 8.429GHz with the help of liquid nitrogen and helium.
{Note:-
- what is the good processor speed ?
and answer are a good processor speed has nothing to do with the laptop being good overall. A laptop which has a i5 clocked at 3.4Ghz from the 4th generation is still faster than a i5 3.2Ghz from the 6th generation,in your context,but yet,when actual benchmarks start rising,the 6th gen wins.
2. Is an AMD processor better than Intel?
That said, AMD's CPUs, especially at the mid-range and lower-end of the spectrum, do tend to offer slightly better value than Intel's chips. Conversely, Intel CPUshave stronger single-core and gaming performance than even AMD's best Threadripper CPUs
3. Is AMD better than Intel for gaming?
Both CPUs are good for gaming, but however AMD offers the stuff at a lower price and with Intel, for playing games, you need a GPU, but with the AMD APUs you don't need one, they are made for gaming (contains CPU+GPU)…. But still the performance differs at different types of games.}
Graphic
Intel Graphics Technology (GT) is the collective name for a series of integrated graphics processors (IGPs) produced by Intel that are manufactured on the same package or die as the central processing unit (CPU). It was first introduced in 2010 as Intel HD Graphics.
Intel Iris Graphics and Intel Iris Pro Graphics are the IGP series introduced in 2013 with some models of Haswell processors as the high-performance versions of HD Graphics. Iris Pro Graphics was the first in the series to incorporate embedded DRAM.
In the fourth quarter of 2013, Intel integrated graphics represented, in units, 65% of all PC graphics processor shipments. However, this percentage does not represent actual adoption as a number of these shipped units end up in systems outfitted with discrete graphics cards.
Note :-
Do all Intel processors have integrated graphics?
Do all Intel processors have integrated graphics?











0 Comments:
Post a Comment